Identifiable characteristics
Western white pine is a medium- to large-sized tree that can grow up to 60 metres high and two metres in diameter and can commonly live to be 300 to 400 years old. It is usually found in closed groups of trees and has a sparse crown and short branches. When the tree is young, its bark is thin, smooth and greyish-green, and it turns darker as the tree ages, forming deep, vertical grooves with small rectangular scaly plates.
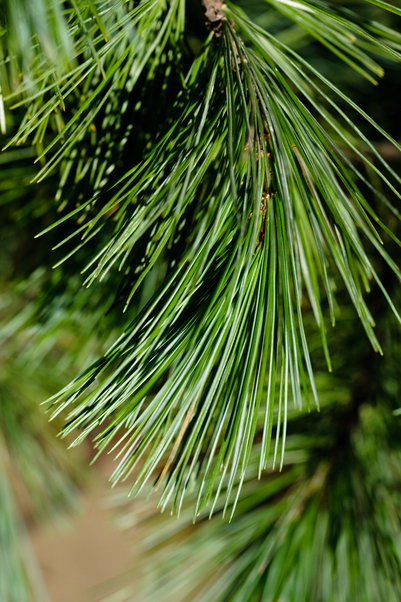
Needles occur in bunches of five, about 5 to 10 centimetres long. Slender, straight and soft to touch, they are bluish-green in colour with a whitish tinge. The edges are very finely toothed. Seed cones are cylindrical when closed, about 10 to 25 centimetres long, and they are on a two-centimetre stalk. The scales are often bent backwards when dry. The seeds have wings about three centimetres long.
Photo credit: Brudder Productions