Identifiable characteristics
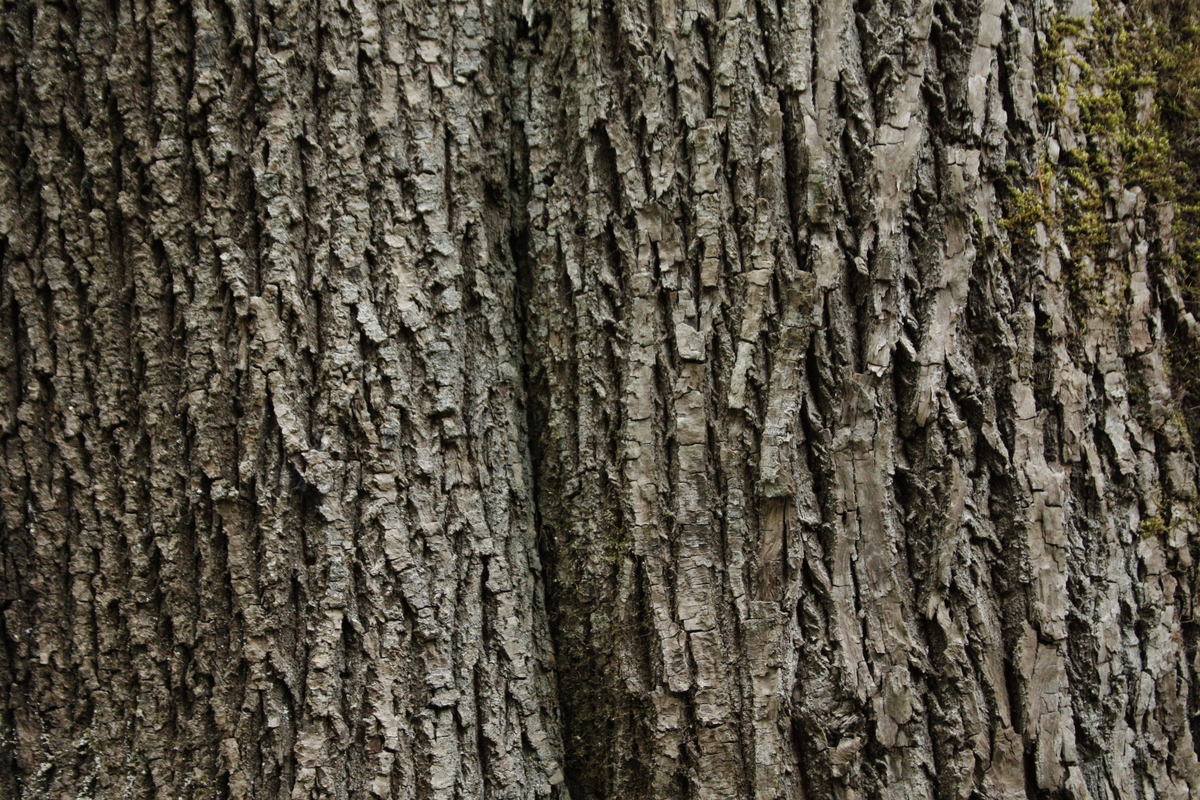
Bigleaf maple, also known as Pacific Coast maple or western maple, is the largest maple tree in Canada, reaching 36 metres in height on good sites. In the forest, it develops a narrow crown that is supported by a stem free of branches for half its length. In the open, it has a broad crown supported by a few large spreading limbs. The bark is greyish-brown and shallowly grooved when the tree is older. The species lives an average of 200 years, with some up to 300 years.
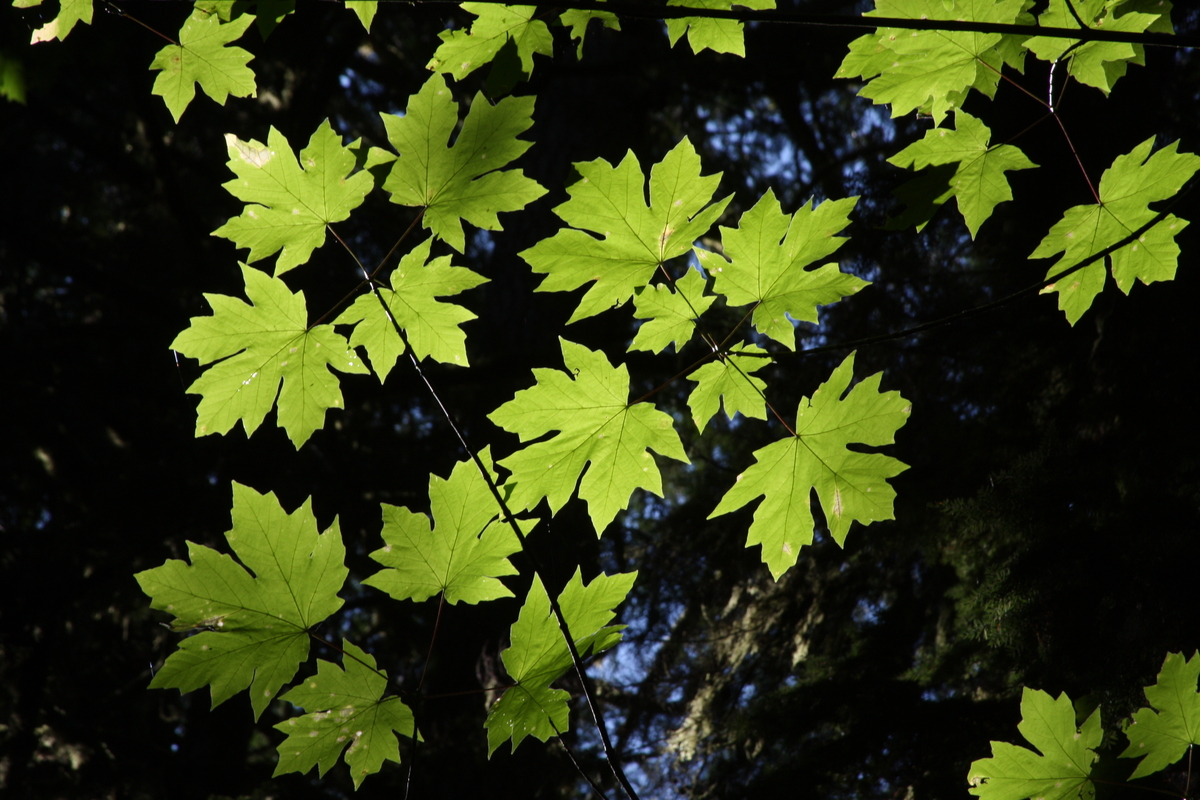
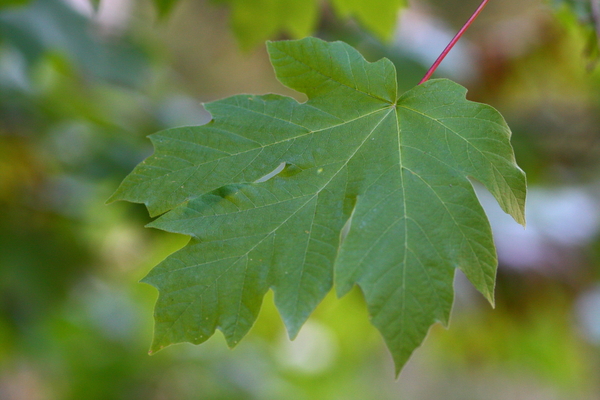
The leaves are the largest of any maple in Canada, measuring 15 to 30 centimetres across. They are deeply five-lobed and have a few blunt, wavy teeth. They are shiny dark green on top and paler underneath and turn yellow in the fall. Small greenish-yellow flowers, about three millimetres across, appear in clusters at the ends of twigs in the spring. The fruit consists of two winged seeds joined at the base, which are three to six centimetres long.
Did you know?
Grain patterns are unsurpassed in some bigleaf maple trees. Occasionally, pieces have highly figured, wavy grain—these include bird’s eye, fiddle-back, blister and curly maple.
Photo credit: Kristin Charleton, Sundew Media